By Erin Rodriguez
Table of Contents
ToggleAs a parent peeks into his daughter’s 3rd grade classroom, he is likely to see several students actively focusing on the teacher, a few more that are doodling randomly, and probably more than one student literally vibrating in their seats, unable to sit still. While each student has his or her own learning style and teachers are employing differentiated learning techniques that address this need, many other students are still struggling to absorb the information being presented. These remaining students may have learning or behavior concerns that have been undiagnosed to this point. Enter RTI.
What is RTI?
RTI stands for Response to Intervention and was implemented in 2004 with the introduction to the Individuals with Disabilities Act (IDEA). Learning and behavior specialists generally consider RTI critical as the first step towards identifying students that may need additional support in the classroom, students with learning disabilities, dyslexia and/or ADHD. Teachers conduct assessments to intervene as quickly as possible, often referring a child for further testing if initial interventions are not enough. The idea is to establish a program for success before any one student falls too far behind.
RTI 3 Tiers
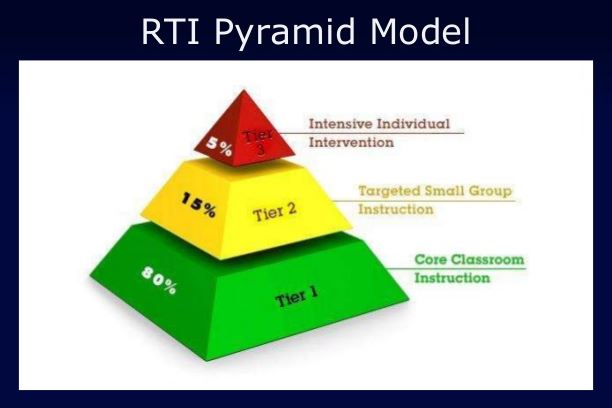
Tier 1 – Core
Tier 1 is conducted in the general education classroom as the teacher checks for the understanding of quality core curriculum and the academic, social, and behavioral progress of each of his students. This universal screening is imperative as struggling students could slip through the cracks if the screening is not conducted thoroughly and appropriately. Many children respond well to the Tier 1 support being performed within the whole classroom and will continue to be successful learners.
Tier 2 – Targeted
Suppose the student doesn’t respond as much as the parents and teacher had hoped? At this point, the student would move to Tier 2. The Tier 2 student will benefit from smaller groups with supplemental instruction that will zero in on student needs as identified by the continued assessment of progress and performance. Successful intervention during this tier includes providing resources and tools for the student to cope and adjust, building confidence by focusing on specific skills that will aid the student in catching up to her peers, and maintaining a solid, organized plan of action based on research-based instruction and assessment.
Tier 3 – Intensive
Occasionally a student needs even more individualized support. Tier 3 of the Response to Intervention model becomes unique to the student’s physical, social, medical, and cultural needs. Instructional strategies are created beyond those that are typically applied to Tier 1 and Tier 2 students. Individualized Education Plans (IEP)are created in this tier by a team of doctors, educators, liaisons, and the parents. There are many options for accommodations to meet the needs of the student’s learning challenges.
Benefits of RTI for Parents and Students
RTI is a fantastic tool for identifying and monitoring learning and behavioral adversities. Because the methodology is flexible, RTI may begin at any age and any point of the school year. The plasticity of the system also allows the student’s interventions and support be modified based on her response to each tier of intervention. This way, each student learns based upon his own skill set and not just that of a whole class or small group. Another, and perhaps one of the best benefits to RTI, is that it can be minimally disruptive so that the student continues to learn the core curriculum. Children respond well to the least amount of disturbance as possible. Finally, parents are able to monitor their child’s progress and can request RTI at any time they feel their student is struggling. As a parent, never hesitate to ask the hard questions and find the right answers. RTI is as much of a tool for parents as for teachers.
The LD Resources Foundation award program was created to help students diagnosed with Dyslexia, ADHD and other learning disabilities. Click here to learn more.


